Table of Contents
- Definition of MLM
- Basic Structure of MLM
- Levels in MLM
- Compensation Plans for MLM
- Common Characteristics of MLMs
- Legal Considerations in MLM
- Advantages of MLM
- Challenges of MLM
- Understanding Network Marketing
- Frequently Asked Questions
Multi-Level Marketing (MLM) is a unique marketing strategy where sellers earn money from both direct product sales and by recruiting new members. The structure consists of various levels, starting with distributors who sell products. As they recruit others, they move up to roles like team leaders and managers, earning a percentage of their recruits’ sales. Compensation plans vary from unilevel to binary structures, determining how commissions are distributed. While MLMs offer low startup costs and flexible schedules, challenges like high attrition rates and market saturation exist. It’s crucial for anyone interested in entering this field to understand these dynamics thoroughly for better success opportunities.
Definition of MLM
Multi-Level Marketing (MLM) is a business model that allows individuals to earn income through the direct sale of products and by recruiting others into the network. In this system, salespersons not only make money from their own sales but also from the sales made by those they recruit, creating a tiered structure often referred to as a “downline.” This structure incentivizes both sales and recruitment, enabling participants to build a network that can generate income from multiple sources. While MLM is sometimes called network marketing or pyramid selling, it’s important to note that legitimate MLMs focus on product sales, distinguishing them from illegal pyramid schemes that prioritize recruitment over tangible goods. For instance, a beauty product MLM might allow members to sell skincare items while also recruiting friends to join their sales team, thus expanding their earning potential.
Basic Structure of MLM
The basic structure of Multi-Level Marketing (MLM) is built around two key components: direct sales and recruitment. In MLM, individuals, often referred to as distributors or representatives, sell products directly to consumers, earning commissions on their sales. This direct selling aspect is crucial, as it allows participants to generate income based on their sales performance.
Recruitment plays a vital role in the MLM model. Distributors are encouraged to recruit new members, creating a hierarchy of salespeople known as a downline. This downline is pivotal for expanding the network and generating additional income. When a distributor recruits someone, they not only gain a new team member but also the potential to earn commissions on the sales made by that recruit. This creates a symbiotic relationship where both the recruiter and the recruited benefit from each other’s sales efforts.
The commission structure is where MLM truly differentiates itself. Participants earn money not only from their direct sales but also from the sales generated by their recruits. For example, if a distributor sells $1,000 worth of products and their downline sells another $2,000, the original distributor can earn a percentage of both amounts. This creates a strong incentive for participants to recruit others and build a successful team, as their income can significantly increase with a larger downline.
In essence, the basic structure of MLM combines the aspects of direct selling and recruitment to create a network of individuals working towards mutual financial success.
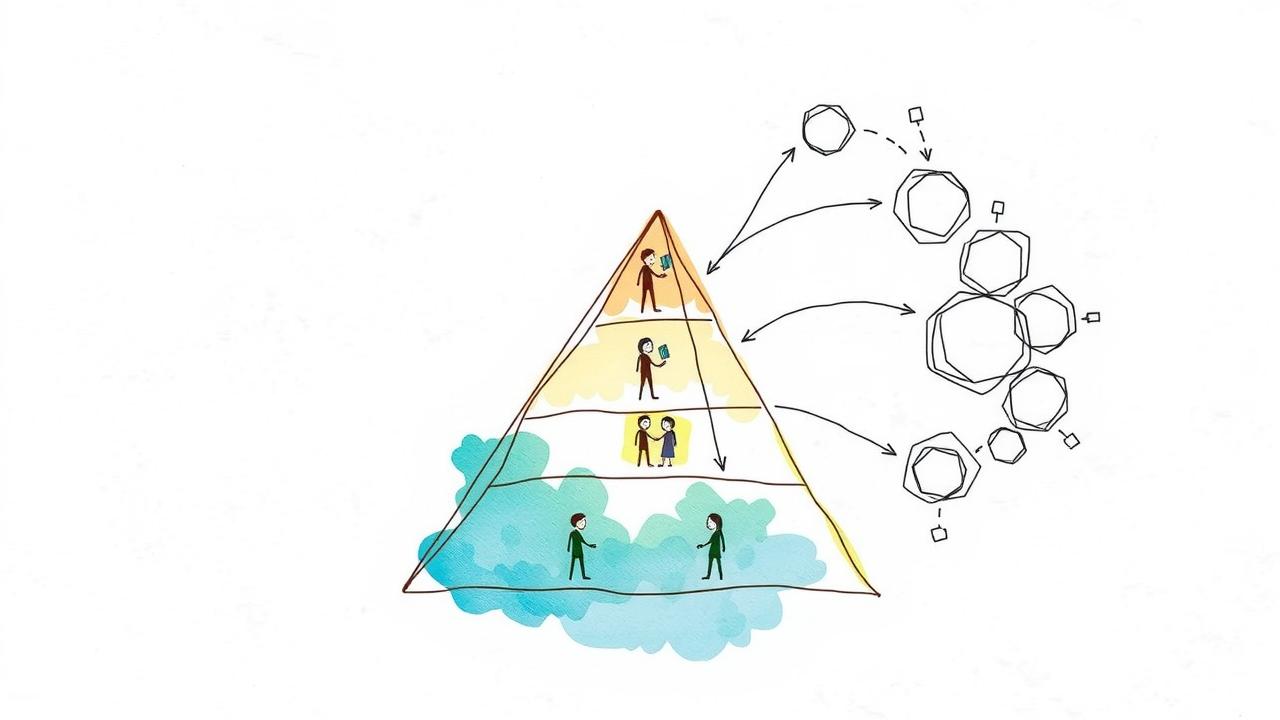
Levels in MLM
In Multi-Level Marketing (MLM), the structure is hierarchical, consisting of various levels that participants can achieve based on their sales performance and recruitment efforts. At the Level 1, known as the Distributor or Representative, individuals start their journey by selling products directly to customers and are incentivized to recruit others. Their earnings are primarily based on commissions from their own sales. Progressing to Level 2, or Team Leader/Supervisor, requires building a small team of distributors. Here, they not only earn from their sales but also receive a percentage of the sales made by their recruits, effectively tapping into a growing network.
As they advance to Level 3, known as Manager or Director, individuals typically oversee a larger team. Their compensation increases significantly, reflecting the performance of their entire downline. At Level 4, the Regional or National Director, leaders manage multiple teams and regions, earning substantial bonuses and a broader percentage of commissions from the organization they have built. Finally, at Level 5, or Executive/Vice President, these top-tier leaders enjoy the highest commissions and bonuses available, thanks to their extensive networks and the success of their teams.
Each level not only offers increased financial rewards but also brings greater responsibilities, including training and mentoring lower-level distributors. This structured approach incentivizes growth while emphasizing the importance of both sales and recruitment in achieving success within the MLM framework.
| Level | Title | Description | Earnings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Distributor/Representative | Entry-level participants who sell products and recruit others. | Earn a commission based on their sales. |
| 2 | Team Leader/Supervisor | Individuals who have recruited a certain number of distributors and trained them. | Earn a commission on their sales and a percentage of sales made by their downline. |
| 3 | Manager/Director | Individuals who have built a substantial team of recruits. | Typically receive higher commissions and bonuses based on the overall performance of their team. |
| 4 | Regional or National Director | High-level leaders overseeing multiple teams or regions. | Earn significant bonuses and a larger percentage of commissions from their entire organization. |
| 5 | Executive or Vice President | Top-tier leaders who have multiple teams under their management. | Receive the highest commissions, bonuses, and incentives from the company. |
Compensation Plans for MLM
 Compensation plans in MLM are crucial as they dictate how participants earn their income. Different structures cater to various strategies and motivations. The Unilevel Plan is straightforward; commissions are earned from direct sales and those of recruits, making it easy to understand. For example, if you sell $1,000 worth of products and your direct recruits sell $500, you earn a commission on both amounts.
Compensation plans in MLM are crucial as they dictate how participants earn their income. Different structures cater to various strategies and motivations. The Unilevel Plan is straightforward; commissions are earned from direct sales and those of recruits, making it easy to understand. For example, if you sell $1,000 worth of products and your direct recruits sell $500, you earn a commission on both amounts.
The Binary Plan requires distributors to recruit two people, creating a left and right leg. Earnings are based on the lesser side, encouraging balance. If you have $2,000 in sales on one side and $1,000 on the other, your commissions will reflect the $1,000.
In contrast, the Matrix Plan limits the number of recruits at each level, creating a structured approach to earning. For instance, a 3×3 matrix means you can only have three recruits at your first level, which can increase earnings as you build depth.
Finally, the Hybrid Plan combines elements from various structures, providing flexibility. This approach can help keep distributors motivated, as it offers multiple avenues for earning. Each plan has its nuances, and understanding them is key to maximizing potential income in MLM.
Common Characteristics of MLMs
 MLMs often share several key characteristics that define their structure and operations. One of the most prominent features is a strong focus on product sales. Successful MLMs sell legitimate products or services that fulfill market needs, ensuring that participants can offer real value to customers. This product-centric model is crucial for sustaining credibility and compliance with legal standards, as it differentiates MLMs from illegal pyramid schemes that prioritize recruitment over sales.
MLMs often share several key characteristics that define their structure and operations. One of the most prominent features is a strong focus on product sales. Successful MLMs sell legitimate products or services that fulfill market needs, ensuring that participants can offer real value to customers. This product-centric model is crucial for sustaining credibility and compliance with legal standards, as it differentiates MLMs from illegal pyramid schemes that prioritize recruitment over sales.
Another defining trait is the emphasis on recruitment. MLMs thrive on expanding their network, encouraging existing members to bring in new recruits. This recruitment strategy is vital for growth, as each new member has the potential to contribute to the overall sales and profitability of the organization.
Training and support also play a significant role in the success of MLM participants. Many companies provide extensive training programs designed to equip new recruits with the skills and knowledge they need to excel in sales and recruitment. For example, an MLM might offer workshops, webinars, and one-on-one coaching to help members understand product features, sales techniques, and effective recruitment strategies.
Moreover, the community aspect of MLMs cannot be overlooked. Many participants appreciate the camaraderie and support found within their networks, which can enhance motivation and engagement. Regular meetings, events, and social gatherings foster a sense of belonging and can help individuals stay committed to their goals.
- Emphasis on recruitment over product sales
- Multiple levels of commission earning
- Structured training and support for members
- Use of personal networks for marketing
- Persistence in sales tactics encouraged
- Frequently associated with a buy-in or startup cost
- Complicated structures that can confuse newcomers
Legal Considerations in MLM
One of the critical aspects of multi-level marketing (MLM) is understanding the legal framework that governs these businesses. MLMs must clearly differentiate themselves from illegal pyramid schemes, which primarily focus on recruitment rather than the sale of actual products or services. In a legitimate MLM, the emphasis should be on product sales, with recruitment serving as a secondary avenue for income. Regulatory bodies, such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States, actively monitor MLM practices to ensure they comply with existing laws and protect consumers from deceptive practices. For example, the FTC has taken action against companies that misrepresent potential earnings or make claims that are unrealistic. Participants should be aware that in order to operate legally, MLMs must provide transparent information about their compensation structure and the income potential of their members. This understanding helps protect individuals from falling into schemes that may seem lucrative but are, in reality, unsustainable and illegal.
Advantages of MLM
 Multi-Level Marketing (MLM) offers several appealing advantages that make it an attractive option for many individuals seeking flexible income opportunities. One of the most significant benefits is the low startup cost. Unlike traditional businesses that may require hefty investments, joining an MLM often involves minimal fees, making it accessible for a wider range of people.
Multi-Level Marketing (MLM) offers several appealing advantages that make it an attractive option for many individuals seeking flexible income opportunities. One of the most significant benefits is the low startup cost. Unlike traditional businesses that may require hefty investments, joining an MLM often involves minimal fees, making it accessible for a wider range of people.
Flexibility is another key advantage. Participants can often set their own hours and work at their own pace, making it easier to balance other commitments such as family or a full-time job. This aspect is especially appealing for those who desire a side income without sacrificing their primary responsibilities.
The earning potential in MLM can be quite enticing. Unlike a fixed salary, individuals have the opportunity to earn based on their effort and the size of their network. Successful sales and effective recruitment can lead to significant income streams. For example, a dedicated distributor who builds a strong team and consistently sells products can see their earnings grow exponentially over time.
Moreover, MLMs often provide comprehensive training and support, helping new recruits develop their sales skills and understand the products. This support system can be invaluable, especially for those who may be new to sales or entrepreneurship.
Finally, the sense of community in MLM can be a motivating factor. Many participants enjoy the camaraderie and support from fellow members, which can foster a positive environment for personal and professional growth.
Challenges of MLM
One of the main challenges in MLM is the high attrition rate. Many people join with enthusiasm but leave within a few months due to unmet expectations. This creates a constant turnover that can be discouraging for those who remain. Market saturation is another significant issue. As more individuals join, it becomes increasingly difficult to recruit new members and find customers. This competition can lead to frustration and diminished earnings for existing distributors. Additionally, MLMs often face reputation issues. The association with pyramid schemes leads to skepticism among potential recruits and customers. This negative perception can hinder the growth of an MLM business, making it crucial for companies to establish their legitimacy and emphasize product sales over recruitment.
Understanding Network Marketing
Network marketing, often synonymous with multi-level marketing (MLM), is an approach where individuals use their personal networks to sell products or services and recruit others to do the same. This strategy relies heavily on personal relationships and word-of-mouth promotion. For instance, a person might sell skincare products to friends and family, while also encouraging them to join the business and sell products themselves. This creates a network of distributors, each contributing to the overall sales volume.
One key aspect of network marketing is its emphasis on building a community. Successful marketers often host gatherings, workshops, or online webinars to train and motivate their teams. This sense of camaraderie can be a powerful tool for retention and engagement, as members feel supported and connected.
However, the success of network marketing hinges on the ability to strike a balance between sales and recruitment. Overemphasizing recruitment can lead to perceptions of the business as a pyramid scheme, where the focus is more on bringing in new members than on selling actual products. Transparency about the products being sold is crucial; companies that focus on genuine product offerings are more likely to build trust and sustain long-term growth.
For example, a wellness company might offer a range of health supplements that align with market trends, ensuring that members are selling items that consumers actually want to buy. This can lead to a more sustainable business model, as the focus remains not just on recruitment, but on providing value to customers.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the different levels in MLM and how do they work?
In multi-level marketing, there are various ranks or levels, often based on how many people you’ve recruited and how much sales volume you’ve generated. Each level usually has different requirements, like a certain number of active recruits or sales quotas, and advancing to higher levels can lead to earning more commissions.
2. How does recruitment affect my MLM level?
Recruitment is key in MLM. The more people you bring into the business, the greater your potential to move up the levels. Your recruits also build their own teams, which can help you earn additional income through commissions on their sales.
3. Can I control how quickly I move up in my MLM?
Yes, you can influence your progress in MLM. By actively selling products and recruiting new members, you can meet the necessary goals to advance. However, it also depends on how your downline performs, as their success impacts your level.
4. What’s the significance of downlines in MLM?
Your downline consists of the people you’ve recruited and their recruits. Their sales contribute to your overall earnings, which can aid in moving up the levels. The success of your downline is crucial since it creates a network that benefits everyone.
5. Do I always need to stay active in my MLM?
Yes, staying active is important in MLM. Many compensation plans require you to maintain certain sales levels or to keep recruiting to stay at your current level or advance further. If you become inactive, you could risk moving down a level.
TL;DR This guide explains Multi-Level Marketing (MLM), which involves earning money through direct sales and recruiting others. It outlines the basic structure, levels from distributors to executives, and various compensation plans like unilevel and binary. Key characteristics, legal considerations, advantages, and challenges of MLM are also discussed. Understanding these aspects is essential for those considering involvement in MLM, ensuring well-informed decisions.